low end tidal co2 after intubation
Here are five things you should know about waveform capnography in cardiac arrest. End-Tidal CO2 in Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation EtCO2 in CPR.

Post Intubation Checklist Airway Inflate Balloon Note Tube Depth
Ensure proper rate approximately 100min Ensure proper depth with adequate releaserecoil of thorax 12 thorax or minimum 25 inches Persistently low EtCO.

. The purposes of this study were to evaluate the clinical utility of a colorimetric end-tidal CO2 ETCO2 detector in confirming proper endotracheal intubation in patients requiring emergency intubation to determine if this new device can be used as an adjunct to judge the effectiveness of cardiopulmonary resuscitation CPR and to determine whether the device. End tidal normally 2-5 mmHg lower than arterial Comparing Arterial and End-tidal CO2 Review of Airway Confirmation Visualization Auscultation. Association between prehospital cpr quality and end-tidal carbon dioxide levels in out-of-hospital cardiac arrest.
End-tidal carbon dioxide reflects CO 2 concentration of alveoli emptying last. B beige indicates moderate levels and probable tracheal intubation. 428 153 mmHg versus 323 141 mmHg.
Normal ETCO2 in the adult patient should be 35-45 mmHg. Capnograph is an indispensable tool for monitoring metabolic and respiratory function. In emergently ventilated trauma patients low end-tidal CO 2 and low cardiac output are associated and correlate with hemodynamic instability hemorrhage abnormal pupils and death.
Alveolar dead space may be increased in most types of lung disease reflecting dysfunction at the alveolar vascular or airway level. A semiquantitative colorimetric FEF end-tidal CO2 detector Fenem Inc New York NY was used to evaluate endotracheal versus esophageal intubation. A high peak of the alveolar phase in poorly compliant lungs.
End-tidal clearance must be evaluated in the context of the patients perfusion status. This will cause a decrease in the ETCO2 end-tidal CO2 and this will be observable on the waveform as well as with the numerical measurement. An ETCO2 below 10 mmHg is associated with poor outcome.
The use of quantitative end-tidal capnometry to avoid inadvertent severe hyperventilation in patients with head injury after paramedic rapid sequence intubation. Maximum end-tidal carbon dioxide Et co 2 within 5 minutes of the onset of mechanical ventilation in the operating room ORBox plot with data points overlaid. Carbon dioxide CO2 along with oxygen O2 share the role of being the most important gases in the human body.
In this study the aim was to review the applications of end-tidal carbon dioxide ETCO2 monitoring in emergency department multiple databases were comprehensively searched with combination of following keywords. 423 20 mmHg versus 34 255 mmHg. This disposable bedside detector registers three ranges of CO2 concentration.
ETCO2 emergency department monitoring and critical. In mmHg the PetCO2 values for those with and without ROSC after five minutes of CPR was. An end-tidal carbon dioxide level of 10 mmHg or less measured 20 minutes after the initiation of advanced cardiac life support accurately predicts death in patients with cardiac arrest associated with electrical activity but no pulse.
The normal values of end-tidal CO 2 is around 5 or 35-37 mm Hg. Though initially there is some CO 2 returning though the tube one finds with subsequent breaths the end tidal graph is lower and lower and the patient is getting more and more hypoxic. The goal should be to maintain ETCO2 no lower than 10-20 mmHg.
The effectiveness of out-of-hospital use of continuous end-tidal carbon dioxide monitoring on the rate of unrecognized misplaced intubation within a regional emergency medical services system. Measurement of a low ETCO 2 value 10 mmHg during CPR in an intubated patient suggests that the quality of chest compressions needs improvement. B beige indicates moderate levels and probable tracheal intubation.
End-tidal carbon dioxide reflects CO 2 concentration of alveoli emptying last. 2 verification of the correct. 11172009 4 Measuring End Tidal CO2 Daltons Law.
78 Nitrogen 21 Oxygen 1 CO2 and other gases Exhaled gases. Loss of ETCO2 may be the first sign that CPR is needed. Negative Epigastric sounds Equal lung sounds Esophageal detector End tidal CO2 detector Secondary signs.
End-tidal CO2 EtCO2 monitoring is a measure of metabolism perfusion and ventilation. End-tidal CO2 ETCO2 detection requires air movement. Dead-space ventilation results in ventilated alveoli with insufficient perfusion which leads to low ETco 2.
MmHg Relate to the air we breath. However EtCO2 is an extremely powerful surrogate for endotracheal tube ETT P osition CPR Q uality R eturn of. Consequently a strategy of high-frequency low-tidal volume breaths will tend to achieve less CO2 clearance for any specific total minute ventilation.
This may result from such ventilatory problems as high mean airway pressure or inadequate exhalation time resulting in overdistention or from such circulatory problems as. Congratulations youre in the oesophagus. Total pressure of a gas is the sum of the partial pressures of the gas Expired CO2 measured PetCO2 mmHg in waveform Percentage Normal Levels PaO2 85-100mmHg PaCO2 35-45mmHg Percentage vs.
Annals of Emergency Medicine. 1 surveillance et monitoring of the intubated patient. In the ED we typically think of a EtCO2 as a marker of perfusion and ventilation.
ETCO2 is one valuable tool we have to tell us that good quality compressions are being delivered. The hinges represent the first and third quartiles the notches represent the 95 confidence interval CI of the median and the whiskers extend to 15 interquartile range. Silvestri S Ralls GA Krauss B et al.
A low P a CO2 level is correlated with increased risk of cerebral edema in children with DKA. Murphy RA Bobrow BJ Spaite DW et al. 1 evaluating the effectiveness of chest compressions and 2 identification of ROSC.
A low end-tidal CO2 in hypothermia. The gradient between the blood CO 2 PaCO 2 and exhaled CO 2 end-tidal CO 2 or PetCO 2 is usually 5-6 mm Hg. The higher the ETCO2 measured during compressions the better the perfusion being supplied by CPR.
Graphically this difference in ROSC vs non-ROSC PetCO2 for both groups appeared to be even greater at ten minutes. For example increased dead space is seen in pulmonary embolism in pneumonia or. Two very practical uses of waveform capnography in CPR are.
A purple indicates low levels and probable esophageal intubation. The measuring of expired CO2at the mouth has solicited growing clinical interest among physicians in the emergency department for various indications.

Waveform Capnography In The Intubated Patient Emcrit Project

Icu One Pager Icu Nurse Critical Care Icu Nursing Critical Care Nursing

Waveform Capnography In The Intubated Patient Emcrit Project

Pin On Free Otorhinolaryngology And Ent Infographics

Waveform Capnography In The Intubated Patient Emcrit Project

Waveform Capnography In The Intubated Patient Emcrit Project

A Systematic Approach To Capnography Waveforms Jems Ems Emergency Medical Services Training Paramedic Emt News

Waveform Capnography In The Intubated Patient Emcrit Project

Vasopressors Demystified An Overview Of The Physiology Of Vasopressors Including When To Start When To Use Periphera Icu Nursing Icu Icu Nurse Critical Care

How To Read And Interpret Capnography Waveforms Infinium Medical
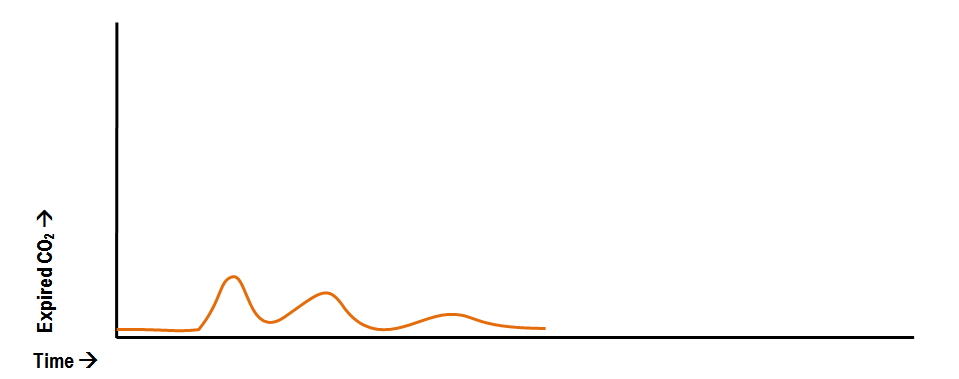
Abnormal Capnography Waveforms And Their Interpretation Deranged Physiology

Nasal Oxygen Delivery Icu Nurse Critical Care Icu Nursing Charting For Nurses

Waveform Capnography In The Intubated Patient Emcrit Project

Etco2 Tutor By Satish Deopujari Tutor Telemedicine Learning

Reversible Causes Of Low Etco2 In Cpr Criticalcarenow

3 Things To Know About Capnography And Advanced Airways Capnoacademy Capnoacademy


